Today, we are going to discuss a very interesting case, which one of our surgeons came across last week. A 56 year old male presented with swelling around ankle on the day of injury. He had twisted his ankle. After the X-ray, it was diagnosed as Comminuted fracture medial malleolus with comminuted fracture fibula shaft. The surgeon planned to treat him with Open reduction & internal fixation through GPC fixLOCK Medial distal tibia plate with tab & Medial malleolus screw fixation. However, intra-operatively, due to unstable ankle injury, the treatment plan was changed.
Clinical History
- 56 year old male
- History of twisting injury around ankle
- Presented on the day of injury
- Pain and swelling over left leg
- Co-morbidities – hypertension
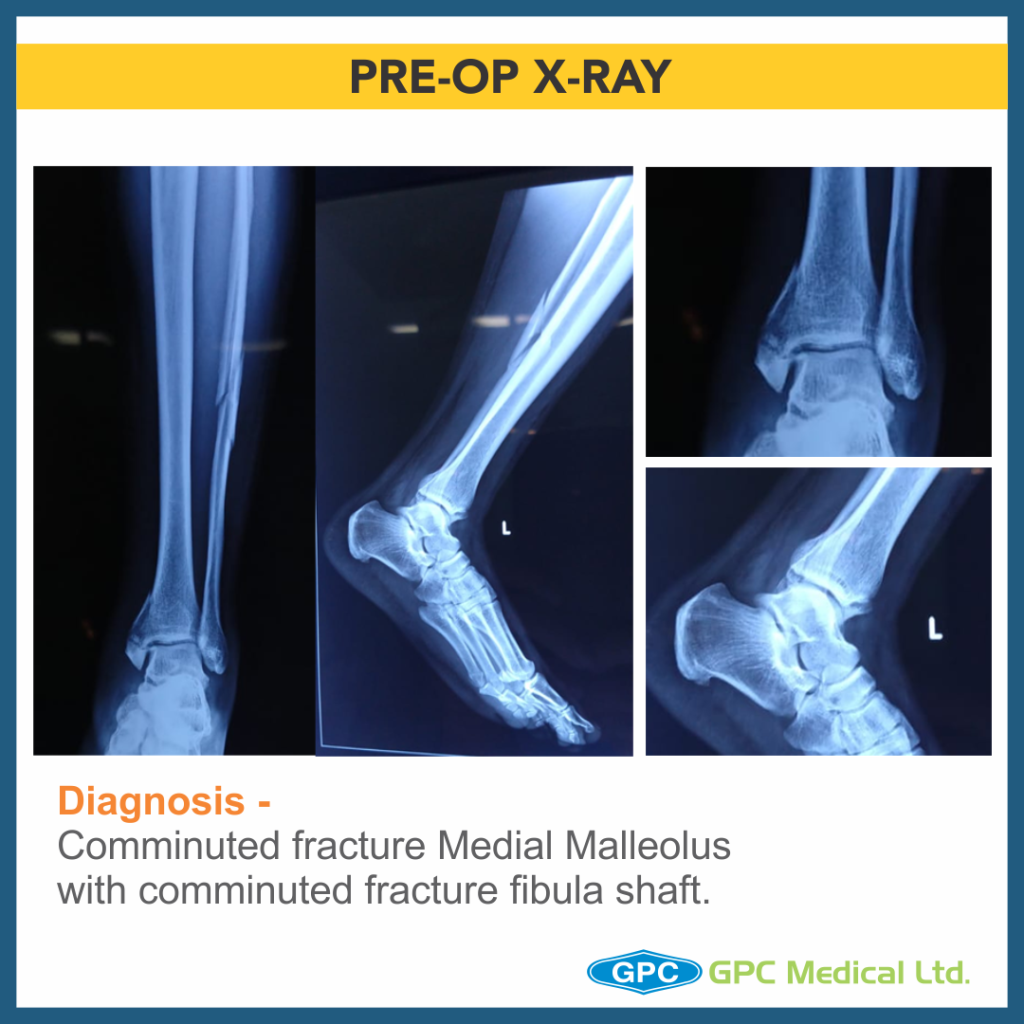
Diagnosis & Treatment Planning
Diagnosis
- Comminuted fracture medial malleolus with comminuted fracture fibula shaft
Plan
- Medial tibial plate with tab
- Medial malleolus screw fixation + neutralization plate
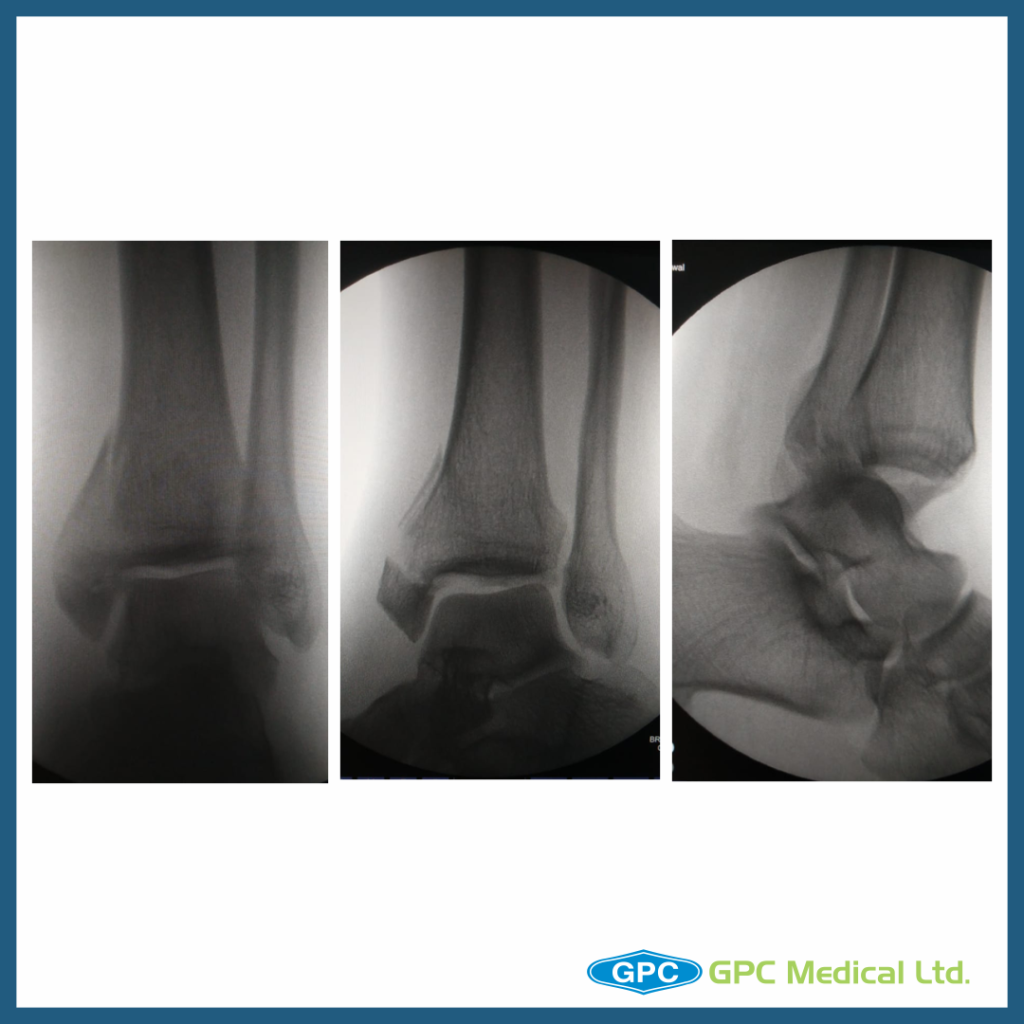
Change in Treatment Planning
Diagnosis
- Comminuted fracture Medial Malleolus (Vertical and Horizontal split) with posterior malleolus fracture with Posterior Subluxation of ankle with comminuted fracture fibula shaft
Plan:
- Medial malleolus screw fixation + neutralization plate
- Stabilization of ankle joint
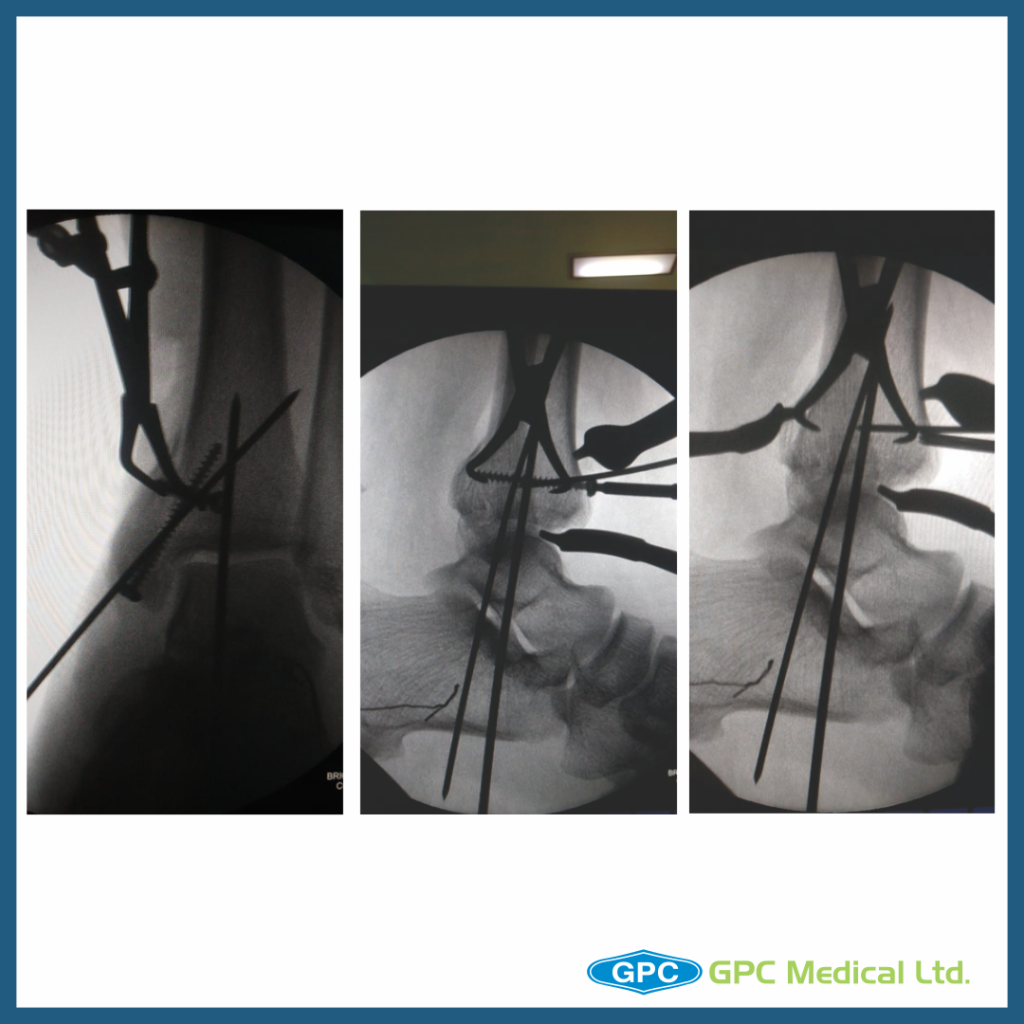
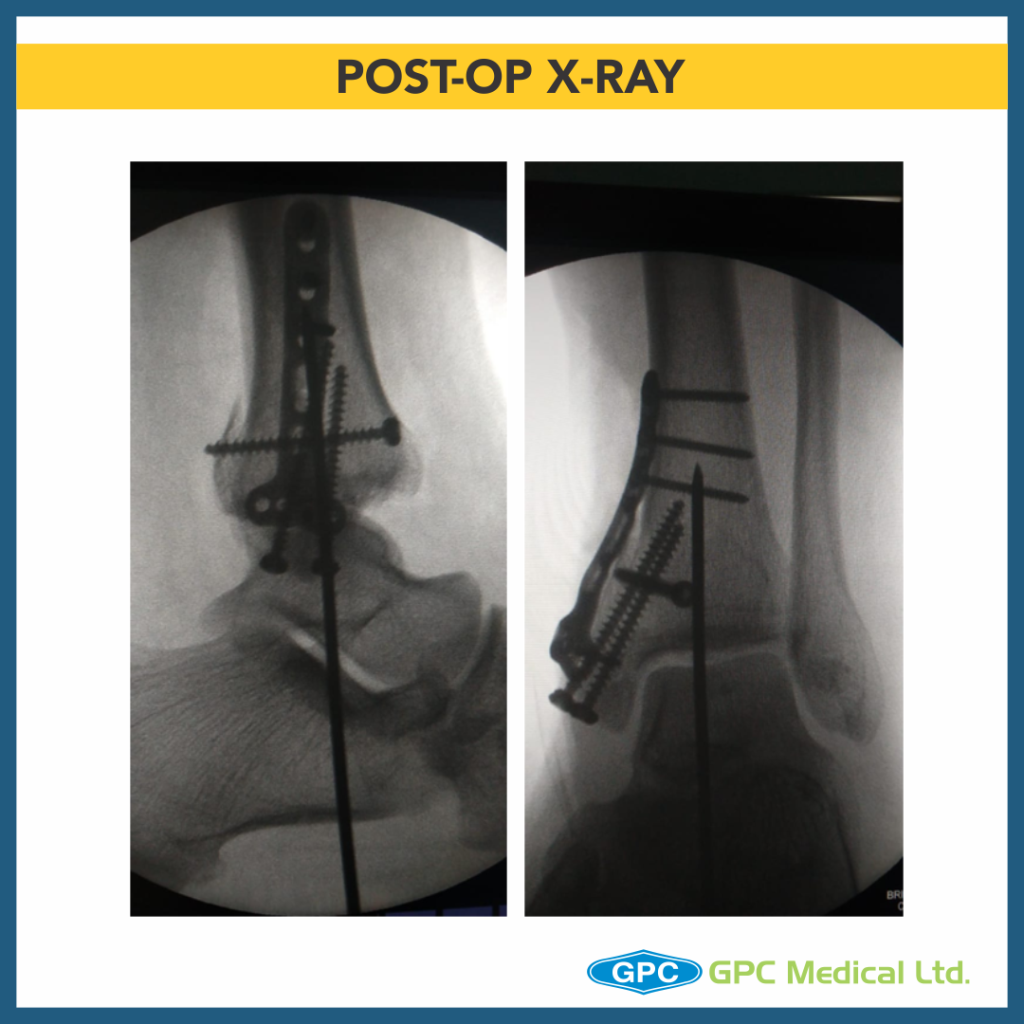
Anatomical reconstruction of joint
- Ankle joint reduced and fixed with K wire
- Posterior malleolus temporarily held with clamp and fixed with screw
- Medial malleolus horizontal split fragment fixed with screws
- Vertical split fragment had numerous small fragments
- GPC Medical Ltd. Distal Radius T-plate used
- Horizontal Limb of T-plate is curved to match the distal tibia and buttress the anterior and posterior aspects
- Volar tilt of T-plate is reversed.
Minimal Soft tissue stripping
Preserved Bone Blood supply
Early return to function