Today, we are going to talk about tibial plateau fractures & metaphyseal defect management after depressed articular fragment elevation.
Management of Periarticular fractures is based in concept of Anatomical reduction of fracture. To allow for primary healing to happen, absolute stability & rigid fixation must be attained. For that sometimes, grafting may be required in defects/gaps in the metaphyseal region.
CASE 1
Clinical Presentation:
– 60 years female.
– Slip and fall at home.
– Severe pain in right knee with restricted knee ROM and inability to weight bear on right leg.
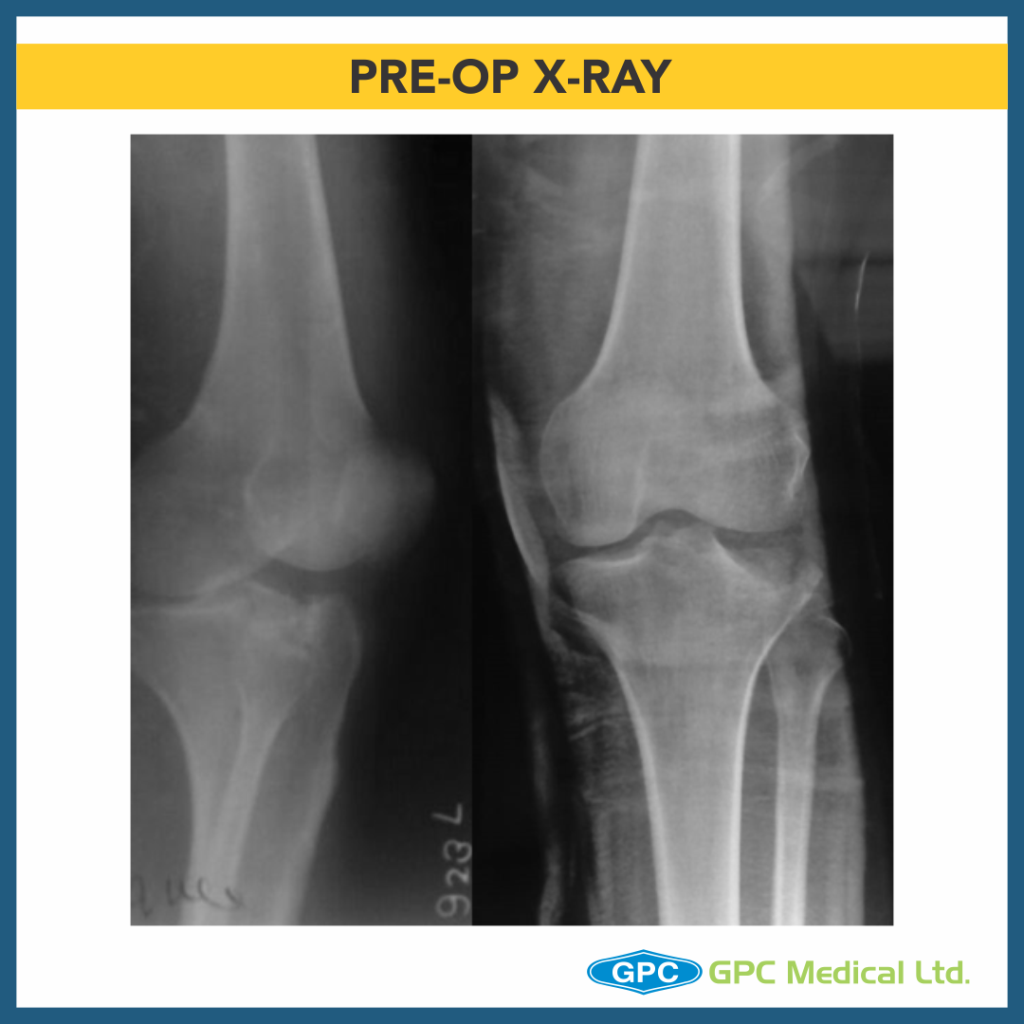
Radiological investigation:
– X-Ray Right knee – Anteroposterior and Lateral Views
Diagnosis:
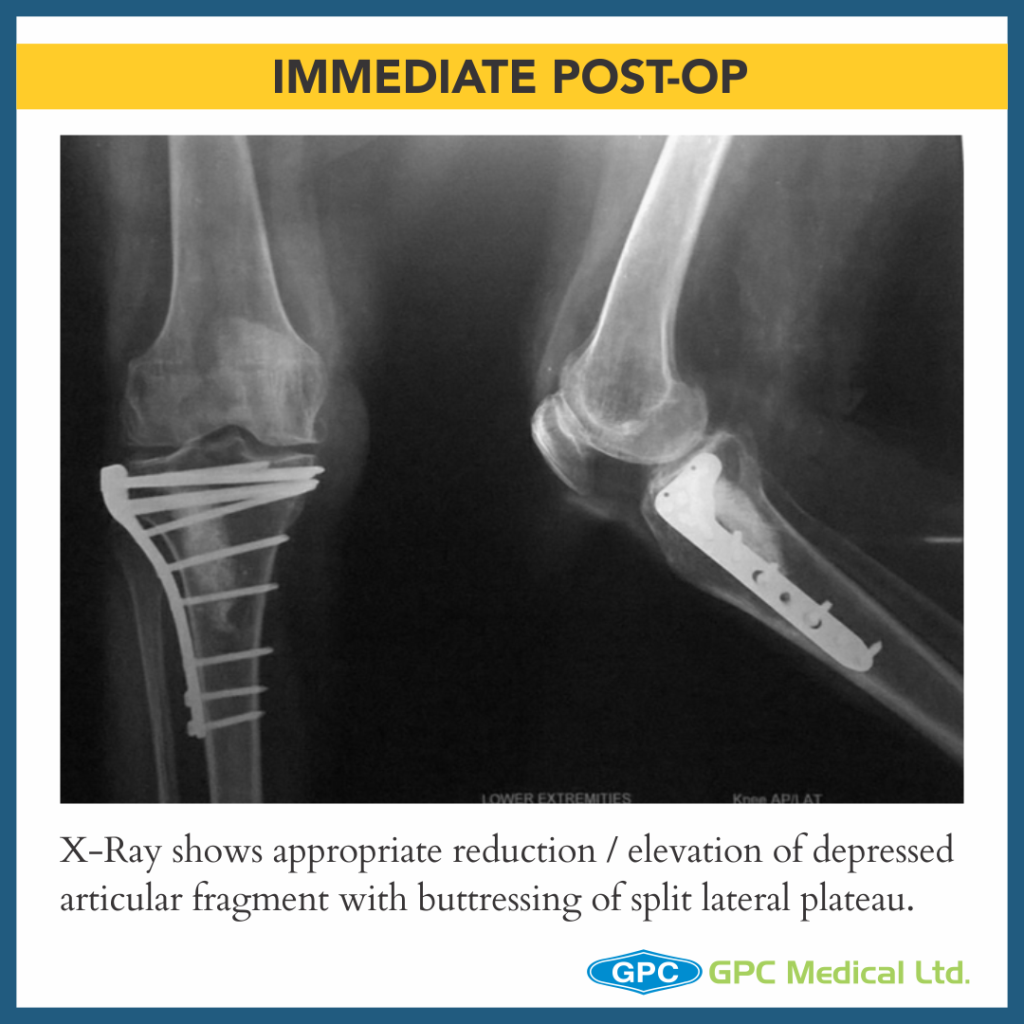
– Split Depression Lateral Tibial Plateau Fractures (Schatzkers Type 2).

CASE 2
Clinical Presentation:
– 59 years Male.
– Alleged history of Road traffic accident.
– Severe pain in right knee with restricted knee ROM and inability to weight bear on right leg.
Radiological investigation:
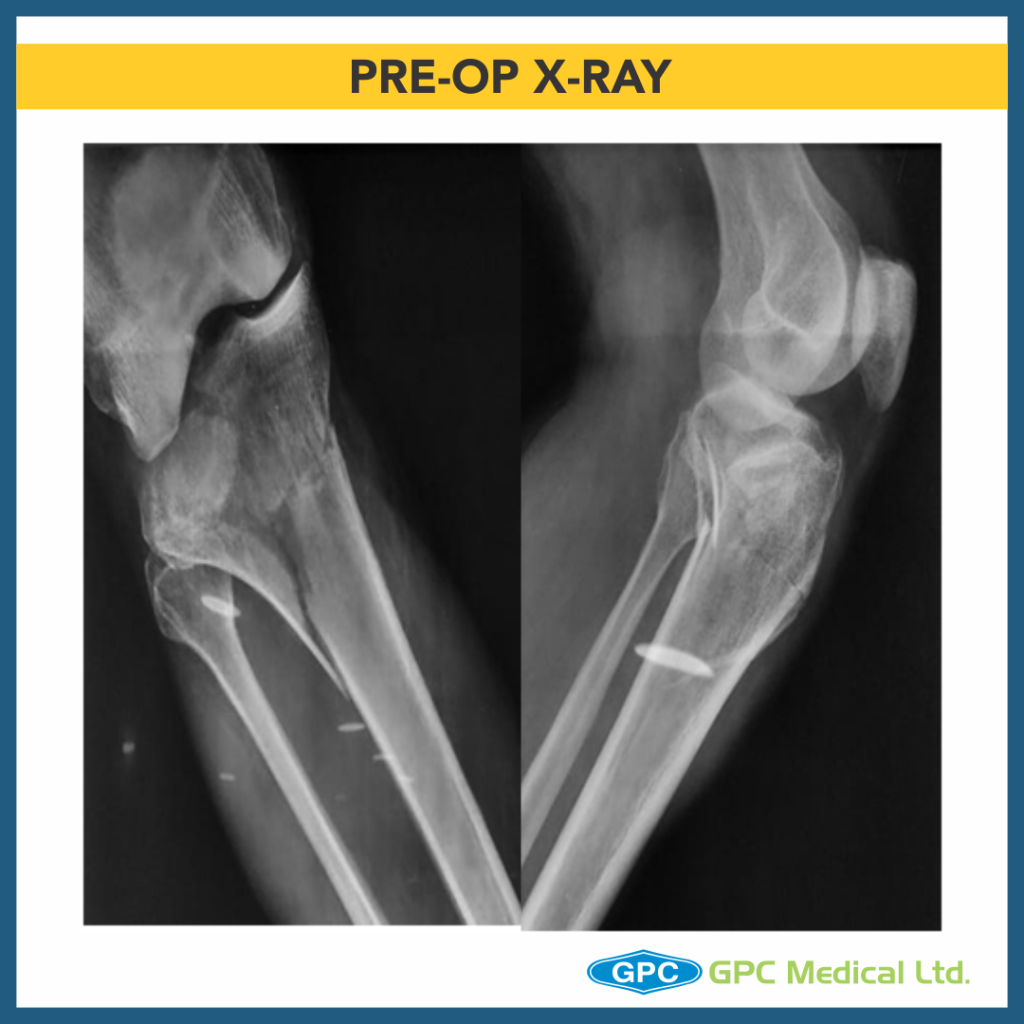
– X-Ray Right knee – Anteroposterior and Lateral Views
Diagnosis:
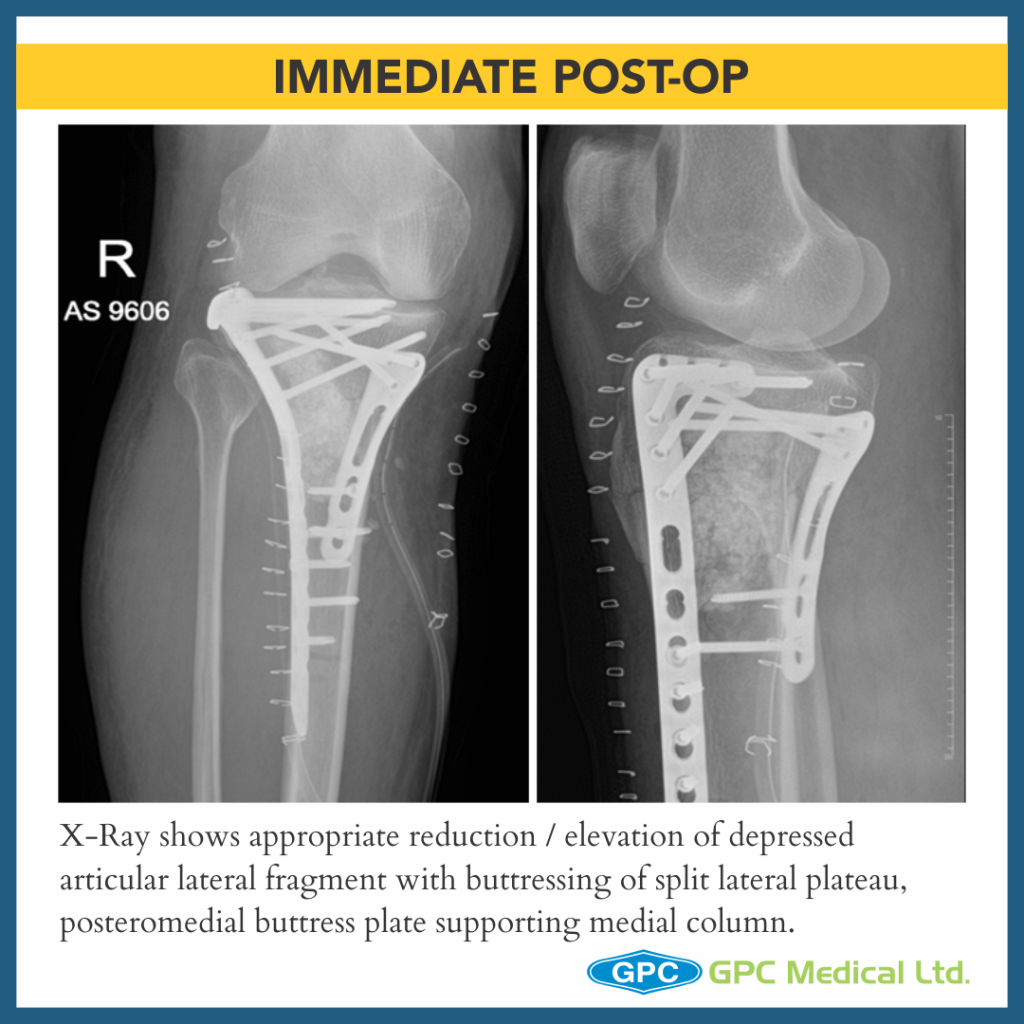
– Medial Plateau Fracture With Split Depression Lateral Tibial Plateau Fractures With Meta-diaphyseal Dissociation (Schatzkers Type 6).

CASE 3
Clinical Presentation:
– 44 years Male.
– Alleged history of Road traffic accident.
– Severe pain in left knee with restricted knee ROM and inability to weight bear on left leg.
Radiological investigation:
– X-Ray Left knee – Anteroposterior and Lateral Views
Diagnosis:
– Split Depression Lateral Tibial Plateau Fractures (Schatzkers Type 2).
CASE 4
Clinical Presentation:
– 18 years Female.
– Alleged history of Road traffic accident.
– Severe pain in left knee with restricted knee ROM and inability to weight bear on left leg.
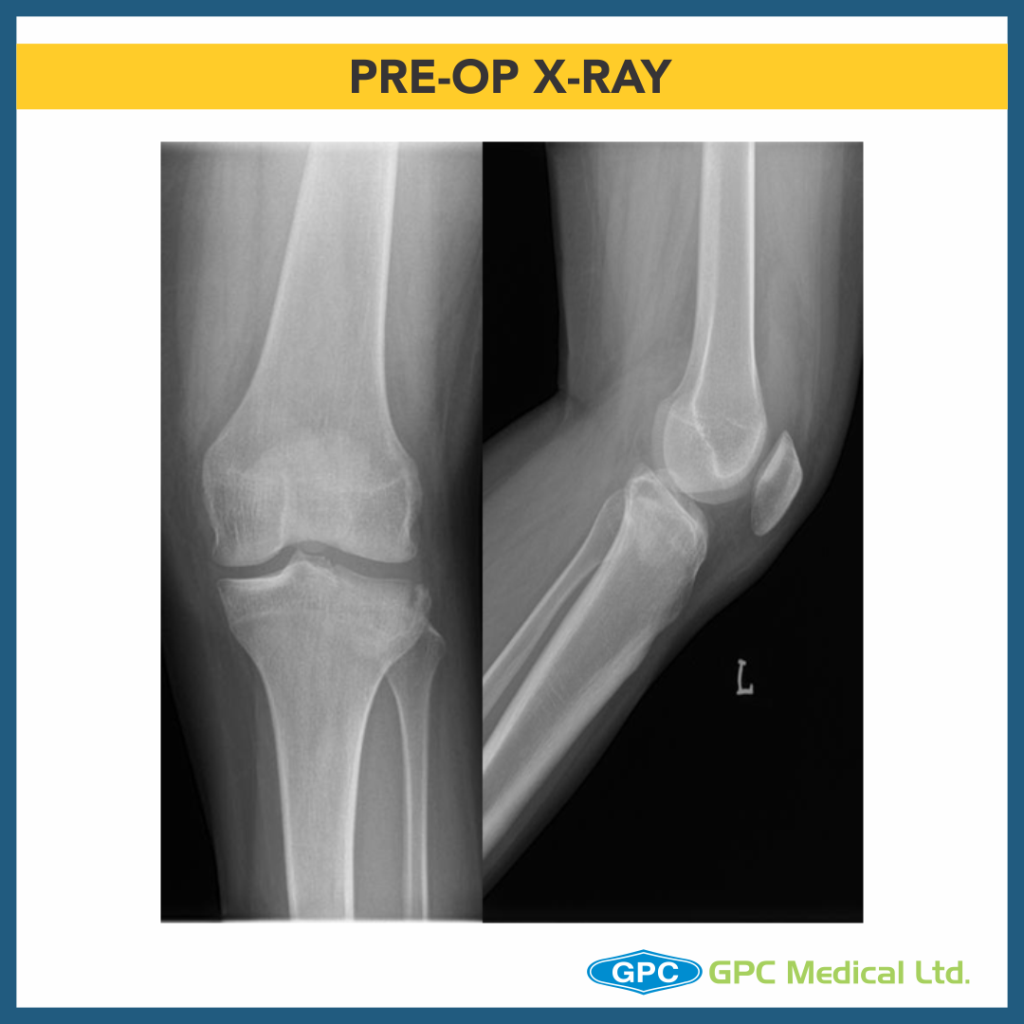
Radiological investigation:
– X-ray Left knee – Anteroposterior and Lateral Views
Diagnosis:
– Depression Type Lateral Tibial Plateau Fractures (Schatzkers Type 3).
CASE 5
Clinical Presentation:
– 29 years Male.
– Alleged history of Road traffic accident.
– Severe pain in right knee with restricted knee ROM and inability to weight bear on right leg.
Radiological investigation:
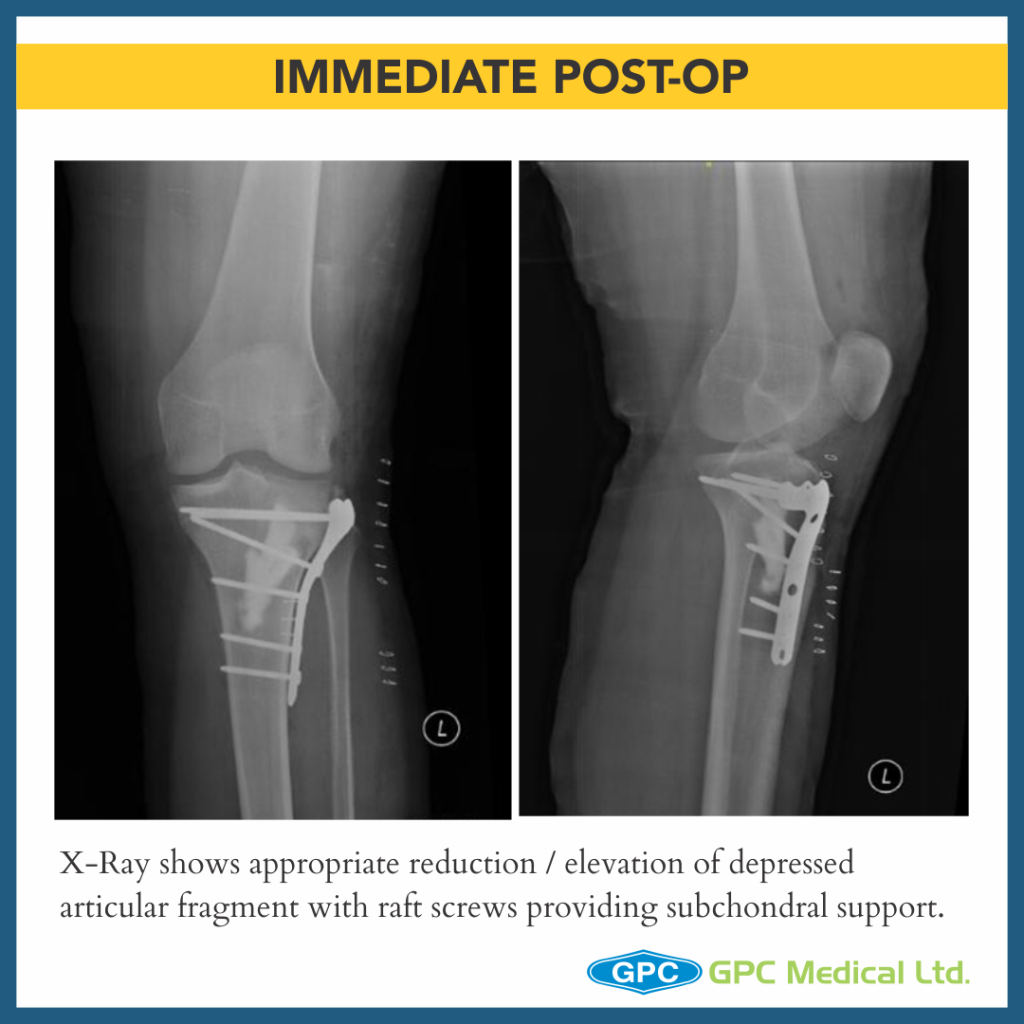
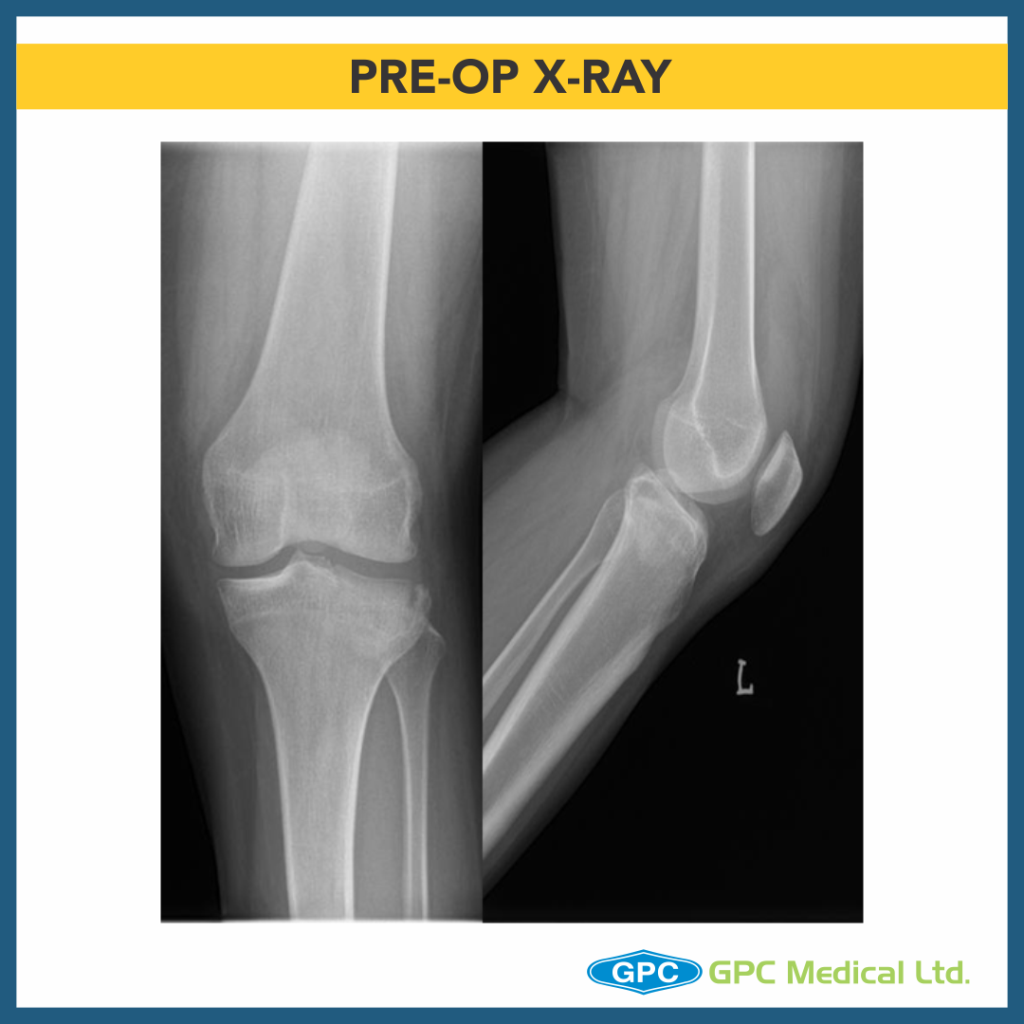
– X-Ray Right knee – Anteroposterior and Lateral Views
Diagnosis:
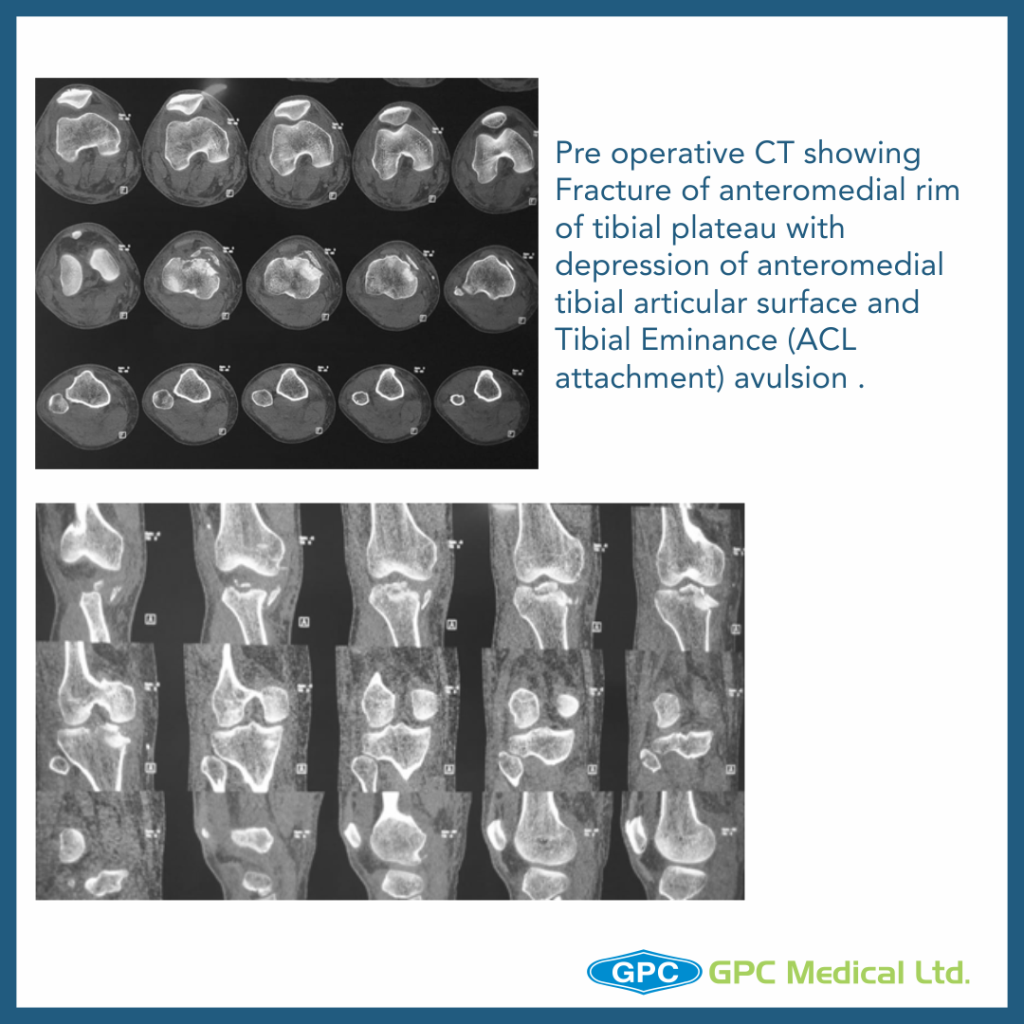
– Split Depression Type Anteromedial Tibial Plateau Fractures with Tibial Eminance (ACL attachment) avulsion.
Surgical Principles and Lacunae in Management
– Principles
- Management for Periarticular Fractures is based on concept of Anatomical reduction of fracture.
- To allow for Primary Bone Healing to happen, Absolute stability and Rigid fixation must be attained.
- Use reduction technique that respects the biological principles of fixation (closed, minimally invasive or open).
- Long term predictor of satisfactory outcome post surgery is restoration of articular suface and mechanical alignment restoration of limb.
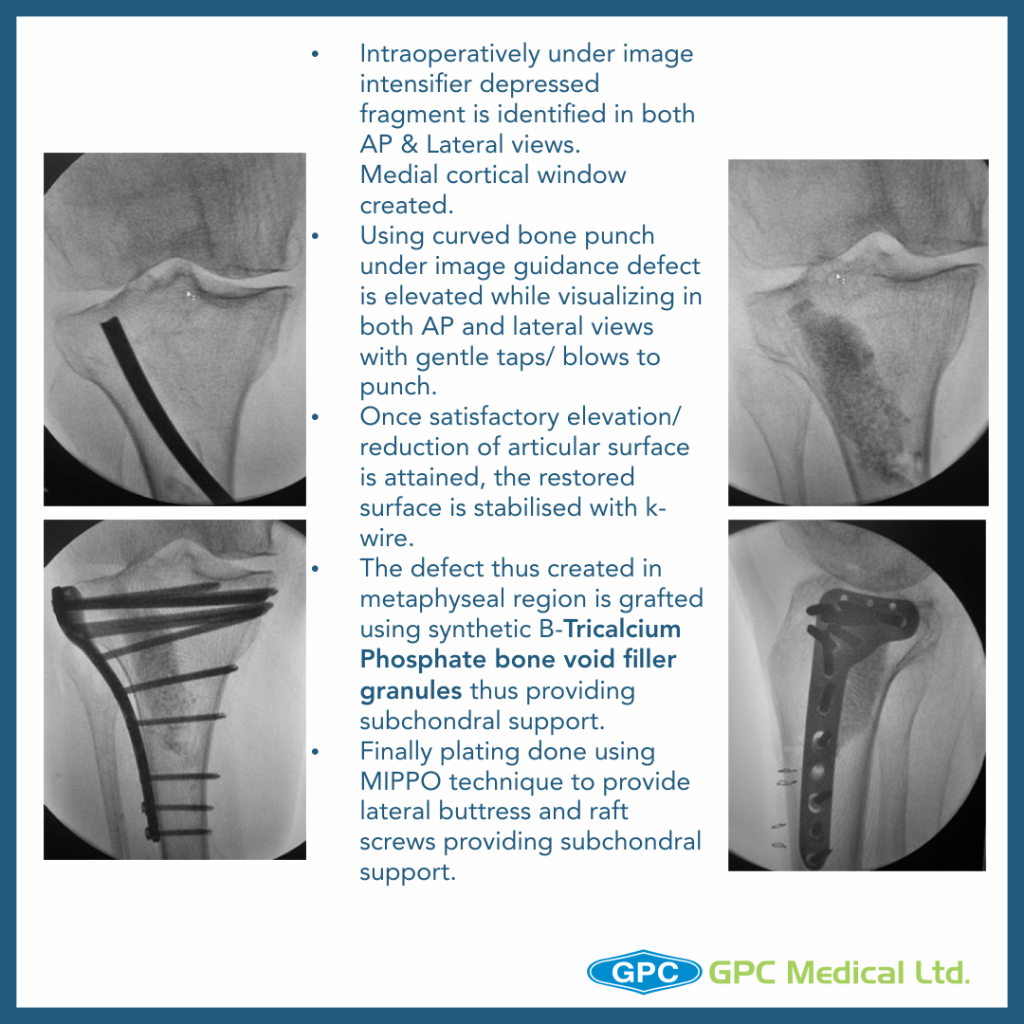
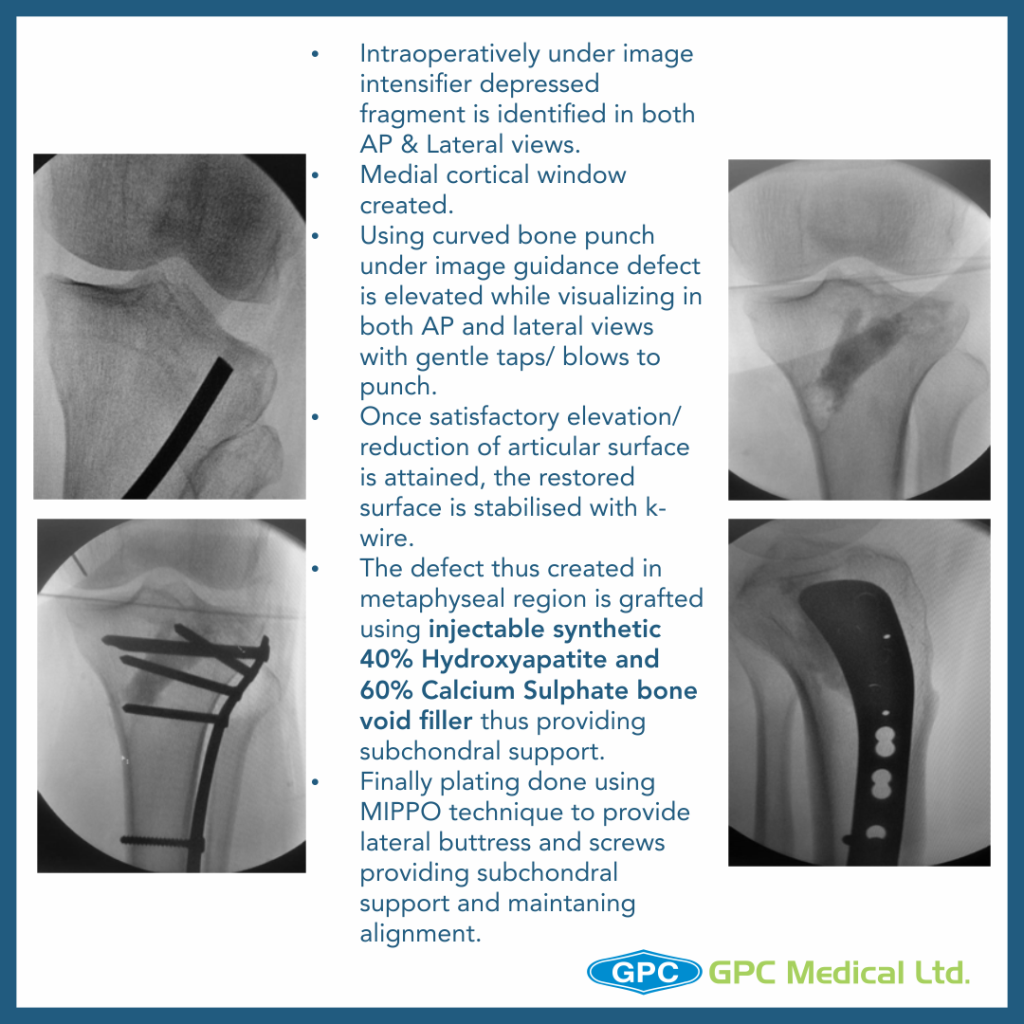
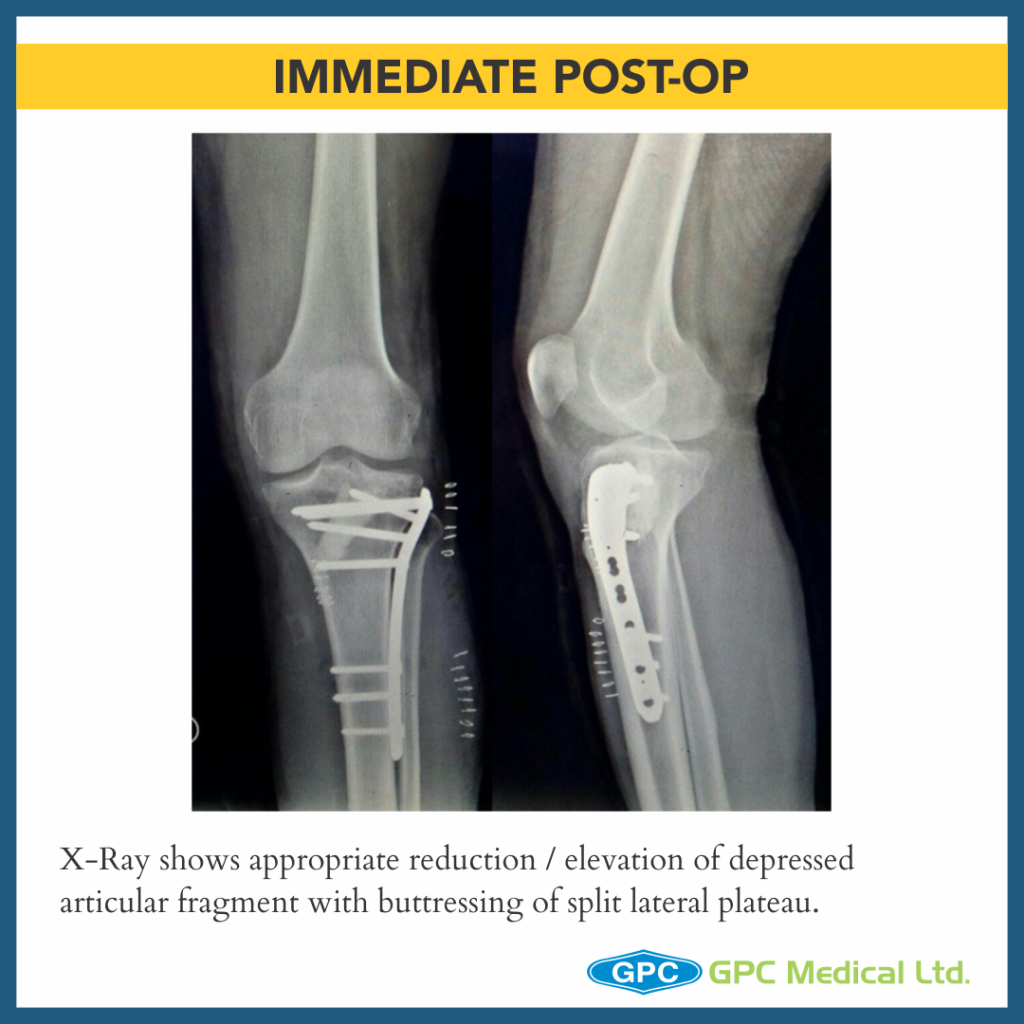
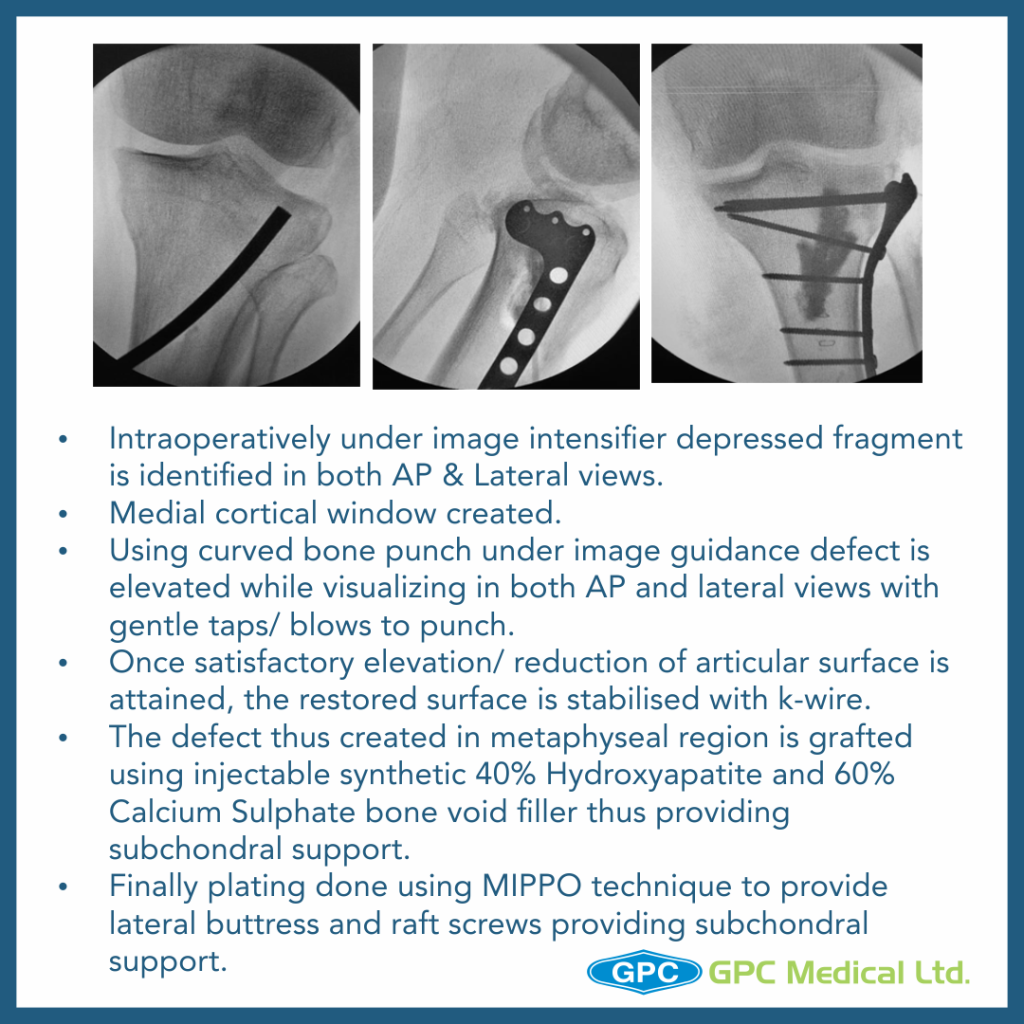
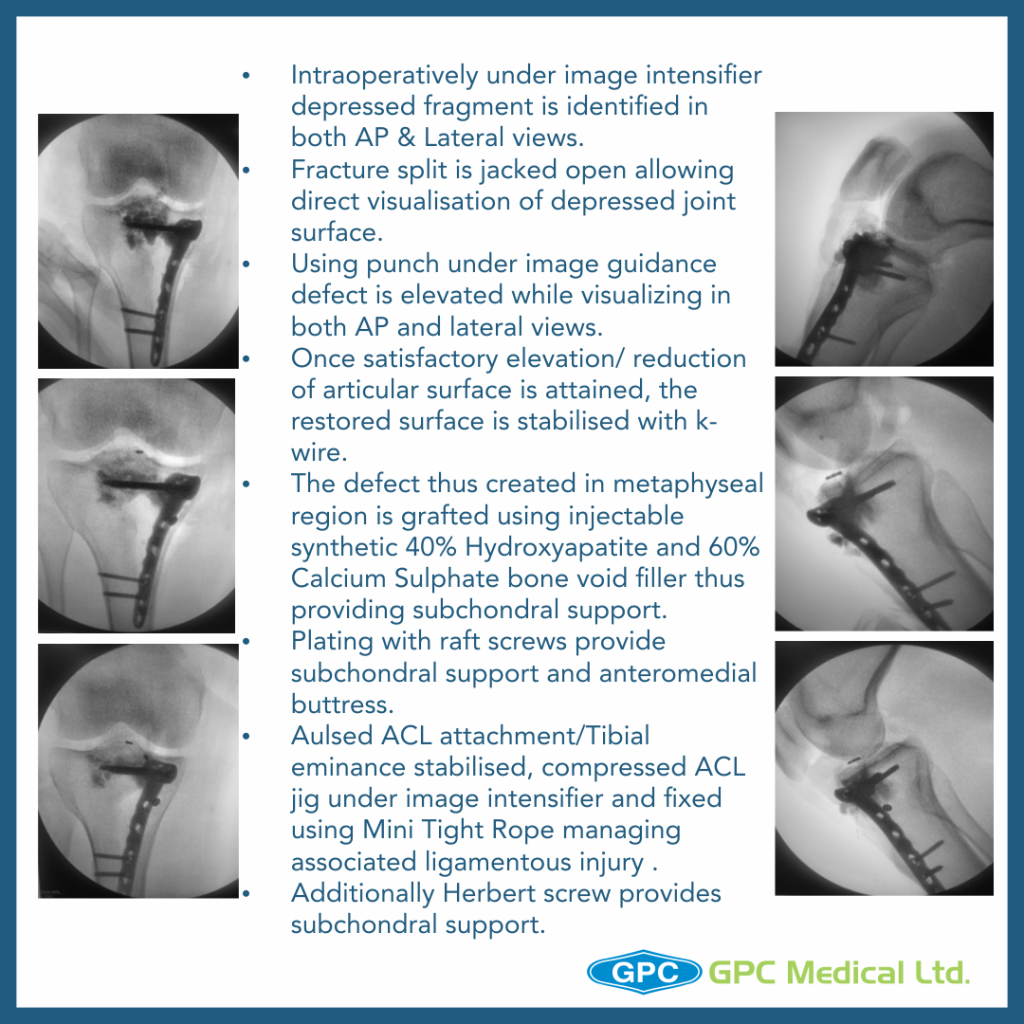
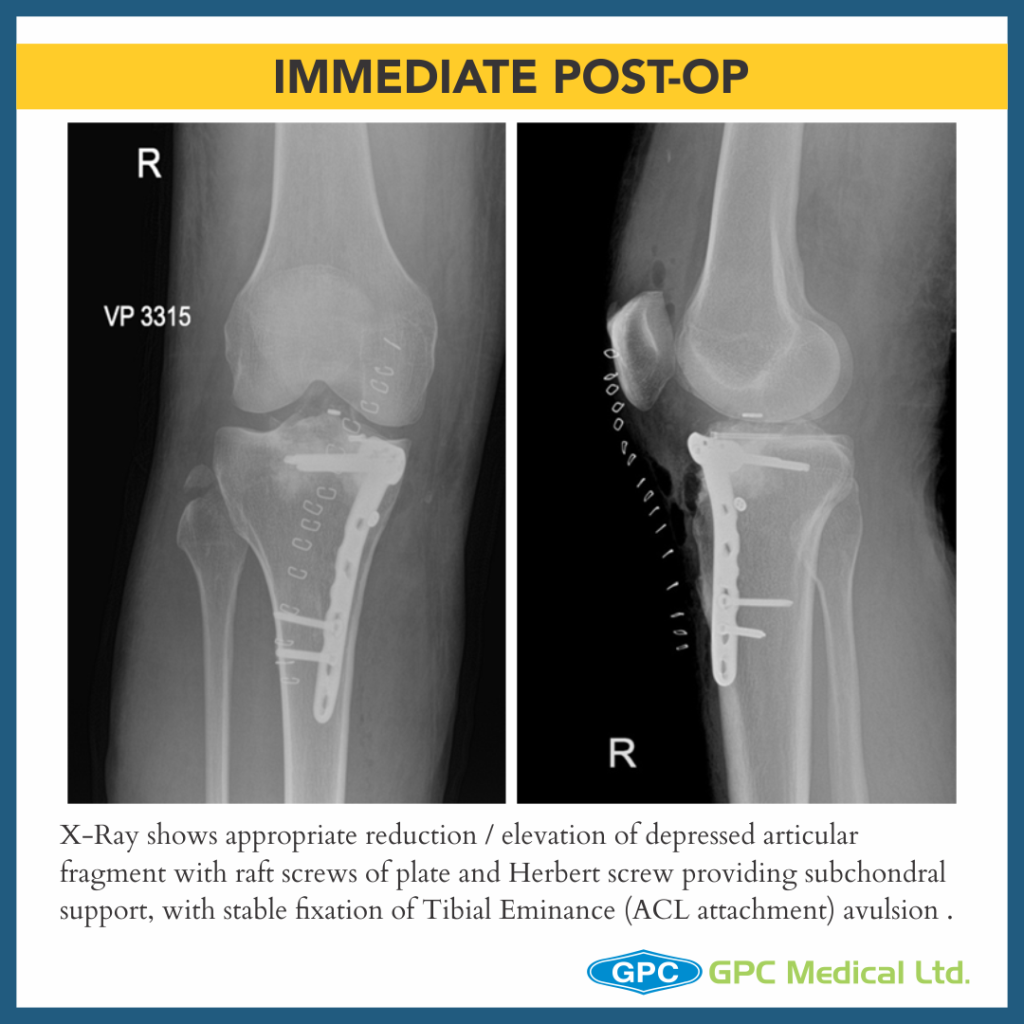
- Once satisfactory elevation/ reduction of articular surface is attained, the restored surface is stabilised with k-wire.
- The defect thus created in metaphyseal region is grafted using either Natural bone graft (Cortcocancellous bone) or Synthetic bone void filler (injectable or granules) thus providing excellent subchondral support.
- These Grafts remodel into host bone within 6-12 months.
- Finally raft screws of plate provide subchondral support and plate help in maintaining the long mechanical axis of limb.
– Lacunae
- Failure to restore articular surface anatomically may result in long term post traumatic arthritis.
- Medial tibial plateau is less forgiving as far as late consequences of a fracture because of smaller meniscus covering joint surface compared to lateral tibial plateau.
